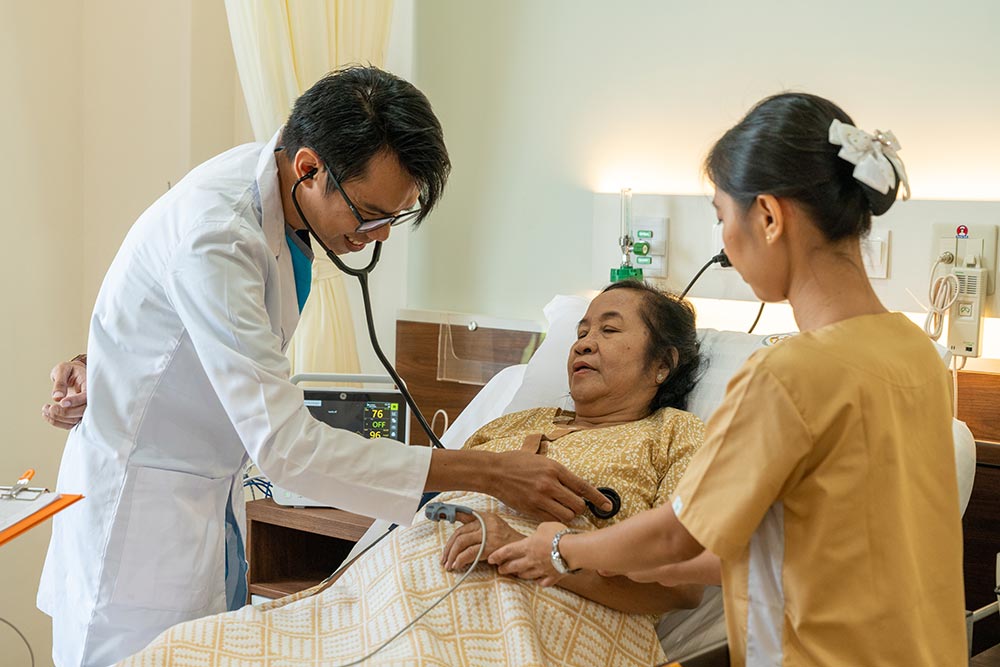
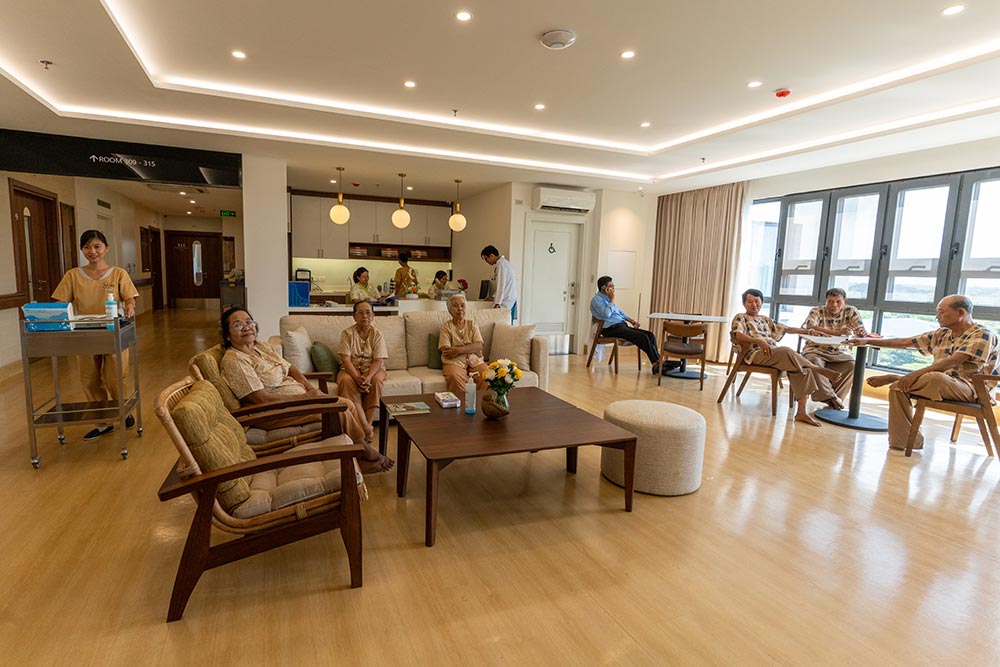
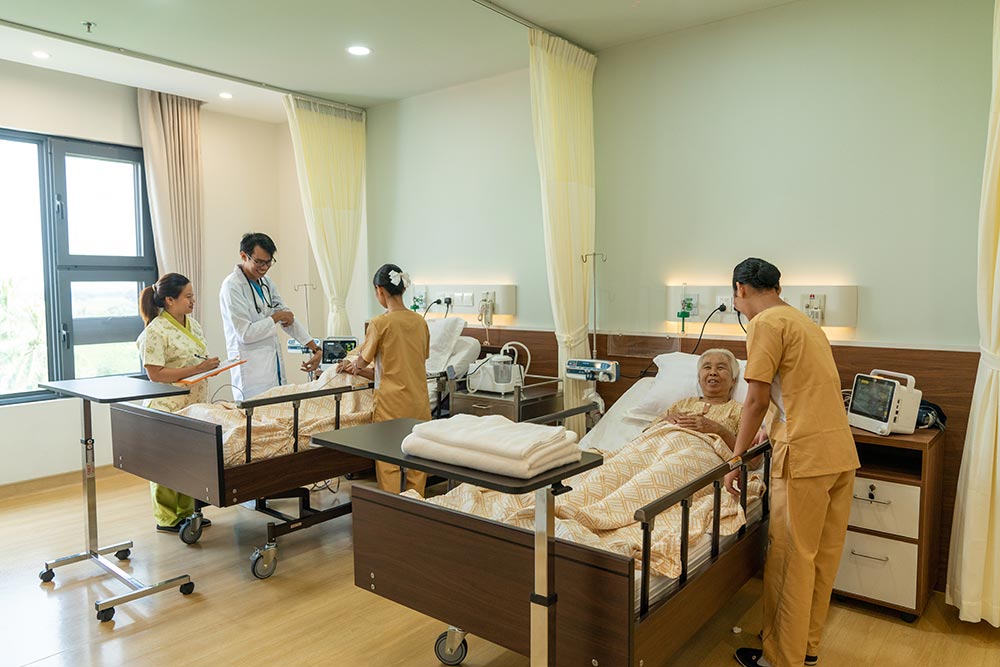
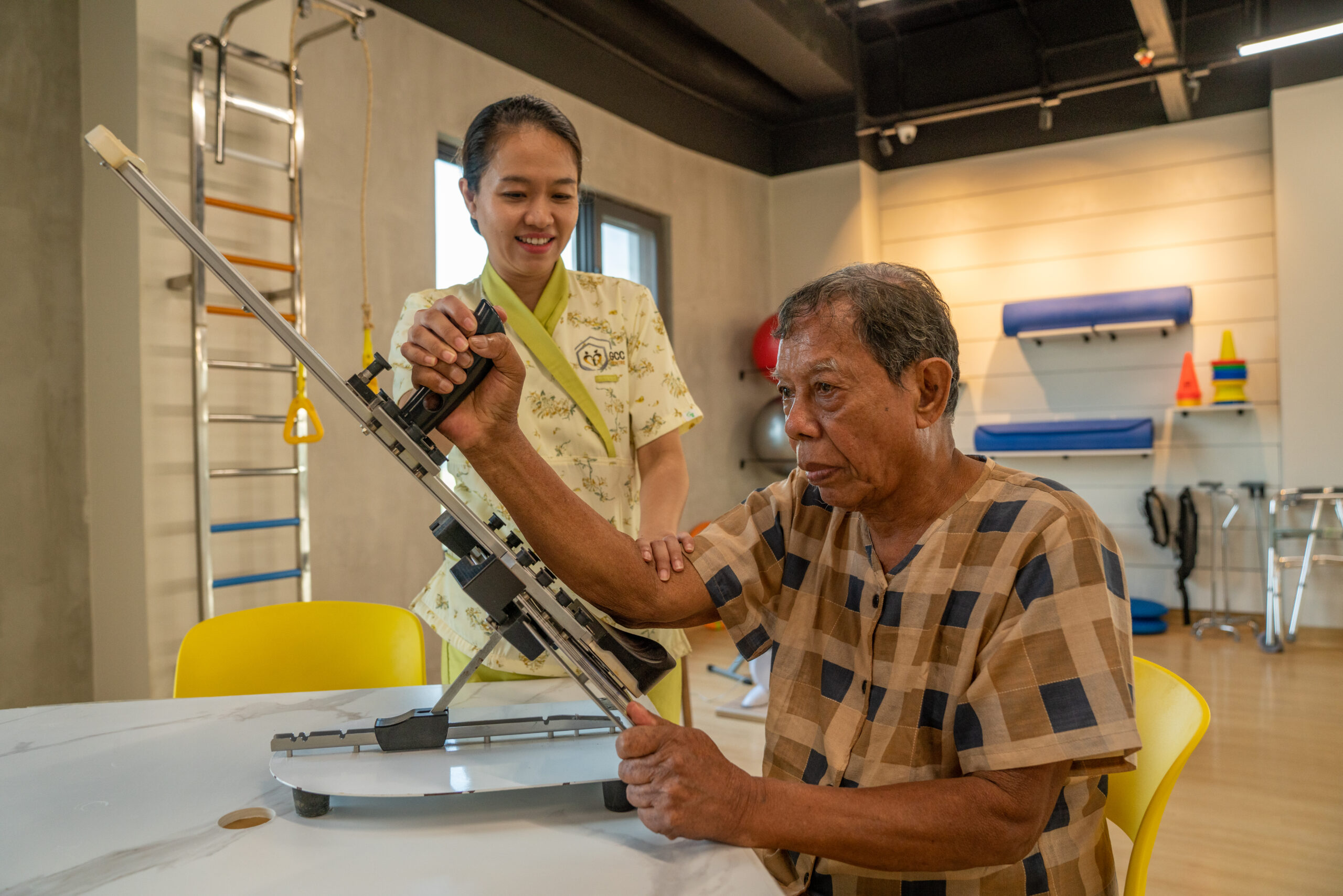
Elderly residents face a variety of risk factors due to the natural aging process and the presence of chronic health conditions. The risk factors in elderly individuals can be physical, psychological, and social. Identifying and addressing these risks is essential for improving the quality of care and preventing complications. Early detection and intervention can significantly reduce the chances of adverse outcomes such as falls, injuries, chronic illness complications, or cognitive decline.
Preventing risk factors requires a comprehensive, individualized approach that considers the physical, cognitive, social, and environmental aspects of care. Implementing preventive measures such as fall prevention, chronic disease management, nutritional support, mental health care, and infection control can greatly improve outcomes for elderly residents. A well-coordinated care plan, staff training, and family involvement are essential components of reducing risk factors and enhancing the overall well-being of elderly individuals.
Falls are one of the leading causes of injury and hospitalization in the elderly. Preventing falls is a high priority in geriatric care centers.
- Balance and Strengthening Exercises: physical therapy programs that focus on improving balance, strength, and flexibility (e.g., tai chi, walking, strength training).
- Assistive Devices: appropriate mobility aids (canes, walkers) and training proper use to enhance stability.
- Environmental Modifications: grab bars in bathrooms, non-slip tiles/mats and adequate lighting to reduce hazards. Keeping hallways clear of obstacles and ensure that flooring is non-slippery and even. Alert systems for residents with limited mobility to call for assistance when needed.
Cognitive decline, including conditions like Alzheimer’s disease and dementia, is common among elderly individuals. Preventing or managing cognitive decline is vital for maintaining quality of life.
Prevention Strategies:
- Mental Stimulation: cognitive exercises, such as puzzles, reading, memory games, and learning activities, to stimulate brain function.
- Social Interaction: socialization by organizing group activities, encouraging conversations, and promoting social engagement to combat isolation and depression, which can worsen cognitive decline.
- Routine and Consistency: predictable daily routine to help residents feel more secure and reduce confusion.
Social isolation can lead to depression, cognitive decline, and other physical health issues.
Prevention Strategies:
- Group Activities: social and recreational activities like arts and crafts, group exercises, movie times, and music sessions to encourage interaction.
- Family Engagement: regular communication with family members through visits, phone calls, or video chats to maintain emotional connections.
- Community Integration: interaction with the larger community through outings, volunteer programs, or intergenerational activities with children or young people.
Poor nutrition and dehydration are common issues in elderly individuals and can lead to weight loss, muscle weakness, and compromised immune function.
Prevention Strategies:
- Balanced Diet: meals rich in vitamins, minerals, and protein, and catering to any special dietary needs (e.g., diabetic-friendly, low-sodium).
- Hydration: regular water intake, especially for residents who have trouble recognizing thirst or have conditions like dementia that reduce their ability to self-monitor hydration.
- Dietary Supplements: nutritional supplements (if necessary) to ensure adequate intake of key nutrients such as calcium, vitamin D, iron, and fiber.
- Assistance with Eating: offering assistance, ensuring meals are easy to chew, and promote social dining to enhance appetite.
Pressure ulcers are a common risk in residents with limited mobility, especially those confined to a bed or wheelchair.
Prevention Strategies:
- Regular Repositioning: routine of turning or repositioning immobile residents every two hours to relieve pressure on vulnerable areas (e.g., hips, heels, back).
- Specialized Mattresses and Cushions: pressure-relieving mattresses or cushions to reduce the risk of bedsores.
- Skin Care: residents’ skin is kept clean and dry, and using moisturizing creams to prevent dry skin.
Mental health issues like depression, anxiety, and delirium are common in elderly individuals.
Prevention Strategies:
- Mental Health Screening: routine screenings for depression and other mental health issues to detect and treat them early.
- Cognitive Stimulation: memory games, reading, puzzles, and other mental exercises to keep the mind active and engaged.
- Relaxation and Stress Reduction: relaxation techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and music therapy to reduce stress and anxiety.
Older adults are more vulnerable to infections, which can lead to serious complications.
Prevention Strategies:
- Vaccination: residents receive the appropriate vaccines, such as flu vaccine.
- Infection Control Practices: strict infection control measures, including hand hygiene, personal protective equipment (PPE) for staff, and environmental cleaning to reduce infection transmission.
- Wound Care: Proper care for wounds to prevent infection and promote healing, especially for residents with diabetes or poor circulation.
Preventing risk factors requires a comprehensive, individualized approach that considers the physical, cognitive, social, and environmental aspects of care. Implementing preventive measures such as fall prevention, chronic disease management, nutritional support, mental health care, and infection control can greatly improve outcomes for elderly residents. A well-coordinated care plan, staff training, and family involvement are essential components of reducing risk factors and enhancing the overall well-being of elderly individuals.